Mangosteen Benefits Explained
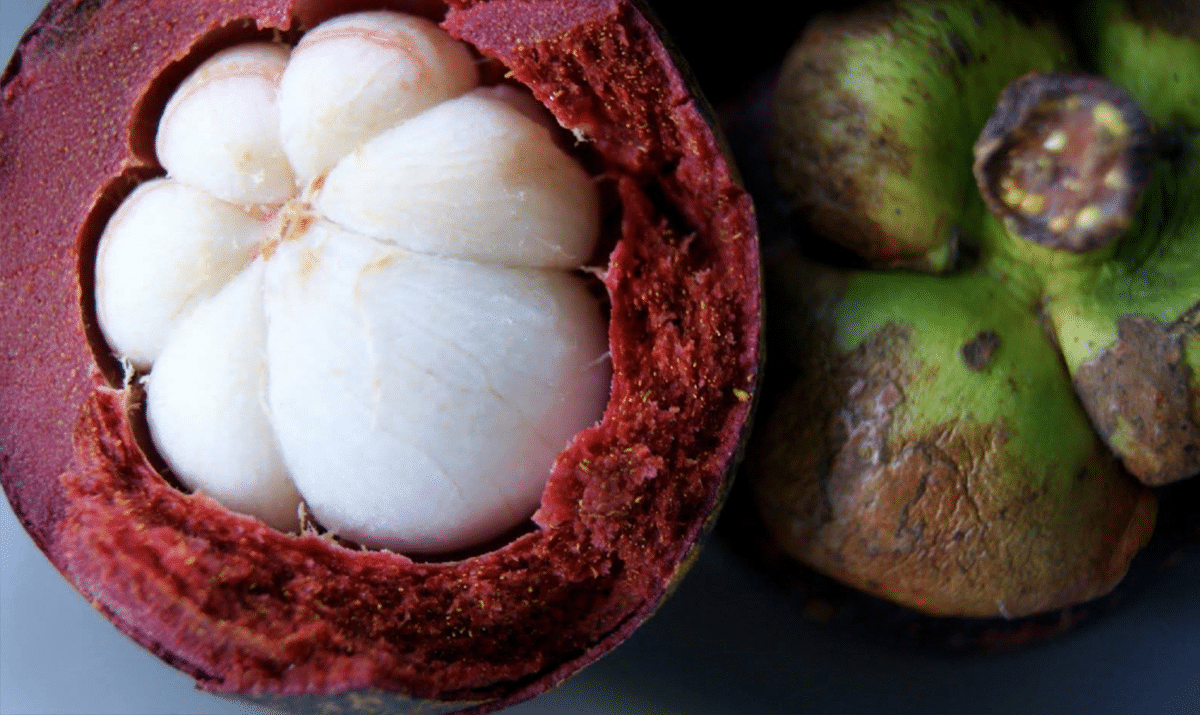
Mangosteen benefits what are they? The mangosteen fruit, Garcinia mangostana, is the size of a passionfruit with a thick purple rind surrounding a snow-white fleshy fruit.

Mangosteen trees have thick, glossy leaves and large, rose-pink flowers. Under favorable conditions, the slow-growing trees can reach a height of 9.5 metres (31 feet).
Mangosteen trees take 8 to 15 years to bear fruit and usually only produce good crops in alternate years.
Where does the mangosteen fruit come from? Mangosteen is native to Southeast Asia and the Malaca Straits area is thought to be its origin. It is the national fruit of Thailand. Currently it is grown in Australia, small pockets of South America and the Caribbean.
Is the mangosteen fruit grown as an environmentally friendly product or is it organically friendly? Look up any of the agricultural literature from orchidists and you will find that, the mangosteen has its own natural defense against pests that includes a yellow latex excreted to cover and destroy pests. Due to this no pesticides or other chemical treatments are needed to grow or harvest mangosteen.
Why is mangosteen so good for you?
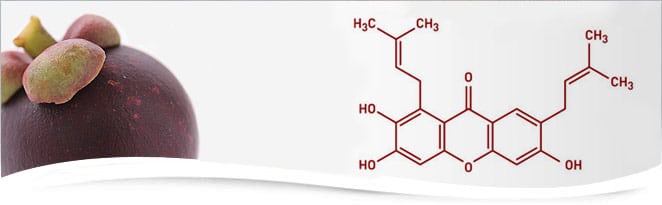
Mangosteen contains 72 known xanthones as at February 2020.
Xanthones are a forgotten nutrient class, capable of unbelievable benefits, no longer found in anything else we might eat or drink.

Not only does mangosteen contain xanthones but it contains other plant nutrients (phytonutrients) such as catechins like those in green tea, polysaccharides like aloe vera and wolfberry in addition to proanthocyanidins similar to those in all red berries.
Mangosteen Nutrients
Several active phytonutrients have been identified in the mangosteen, including:
Xanthones — These powerful compounds demonstrate numerous and beneficial health properties and are the most abundant phytonutrient in the mangosteen**.
Cathechins — These compounds demonstrate antioxidant properties. The mangosteen rind has been shown to have the same level of catechines as found in green tea.
Proanthocyanidins — The same antioxidant benefit touted in grape seed extract, proanthocyanidins are found in efficacious amounts in the whole mangosteen fruit.
Since the discovery of the organic compounds essential to life known as vitamins in the early 1900s, doctors, nutritionists and scientists became interested in the role of food in health and disease. You know that fruits and vegetables contain vitamins and minerals your body needs to function, but the U.S. Department of Agriculture reports on a whole other group of compounds known as phytonutrients now thought to promote good health. One type of phytonutrient known as a xanthone occurs in a variety of plants found in the rain forest, but only one food source is documented to contain xanthones.
Xanthones In Plants
The ONLY known plant containing xanthones that has an edible fruit is, a tropical tree known as Garcinia mangostana.
Scientists extracted two biologically active xanthone compounds from mosses and lichens and a plant found in Madagascar known as Psorospermum cf. molluscum, according to research published in the “Journal of Natural Products.” In this study, xanthone compounds showed promise as being effective in killing tumor cells and helping repair DNA. Because this plant is not a food source, however, the xanthone compound must be isolated from the roots and wood stems. Tropical plants that belong to the group known as Garcinia also contain xanthones. Scientists have studied the extracts of the Garcinia hanburyi plant for its ability to suppress growth by inducing apoptosis, or cell death, according to research published in the “World Journal of Gastroenterology.”
Mangosteen Queen Of Fruits
Garcinia mangostana produces the mangosteen fruit, crowned “The Queen of Fruits” by the people in its native land of Thailand. The people of Southeast Asia use the mangosteen for medicinal purposes; to treat diarrhea, ulcers and inflammation; and to heal wounds. More recently, since scientists discovered that the mangosteen fruit, including the juice, pulp and rind or pericarp, is a rich source of xanthones. It has become one of the three top-selling botanicals in the United States since 2007, according to information published in the “Mini Review of Organic Chemistry.” Research on mangosteen and xanthones shows that this food product may provide health benefits.
Possible Health Benefits of Mangosteen
Information published in the “Nutrition Journal” confirms that two xanthone compounds found in the mangosteen fruit, alpha- and gamma-mangostins, show anti-inflammatory effects. By helping reduce inflammation in the body, xanthones may help reduce the risk for cardiovascular diseases, lung diseases, gastrointestinal diseases and arthritis. Another study published in the “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” reveals that the xanthones in mangosteen inhibit cell growth, a property that makes xanthones a promising agent for cancer prevention. The potential health benefits of the xanthones in the mangosteen fruit along with the presence of other nutrients, including vitamin C, iron, potassium and calcium, make this fruit a potentially healthy addition to your diet.
